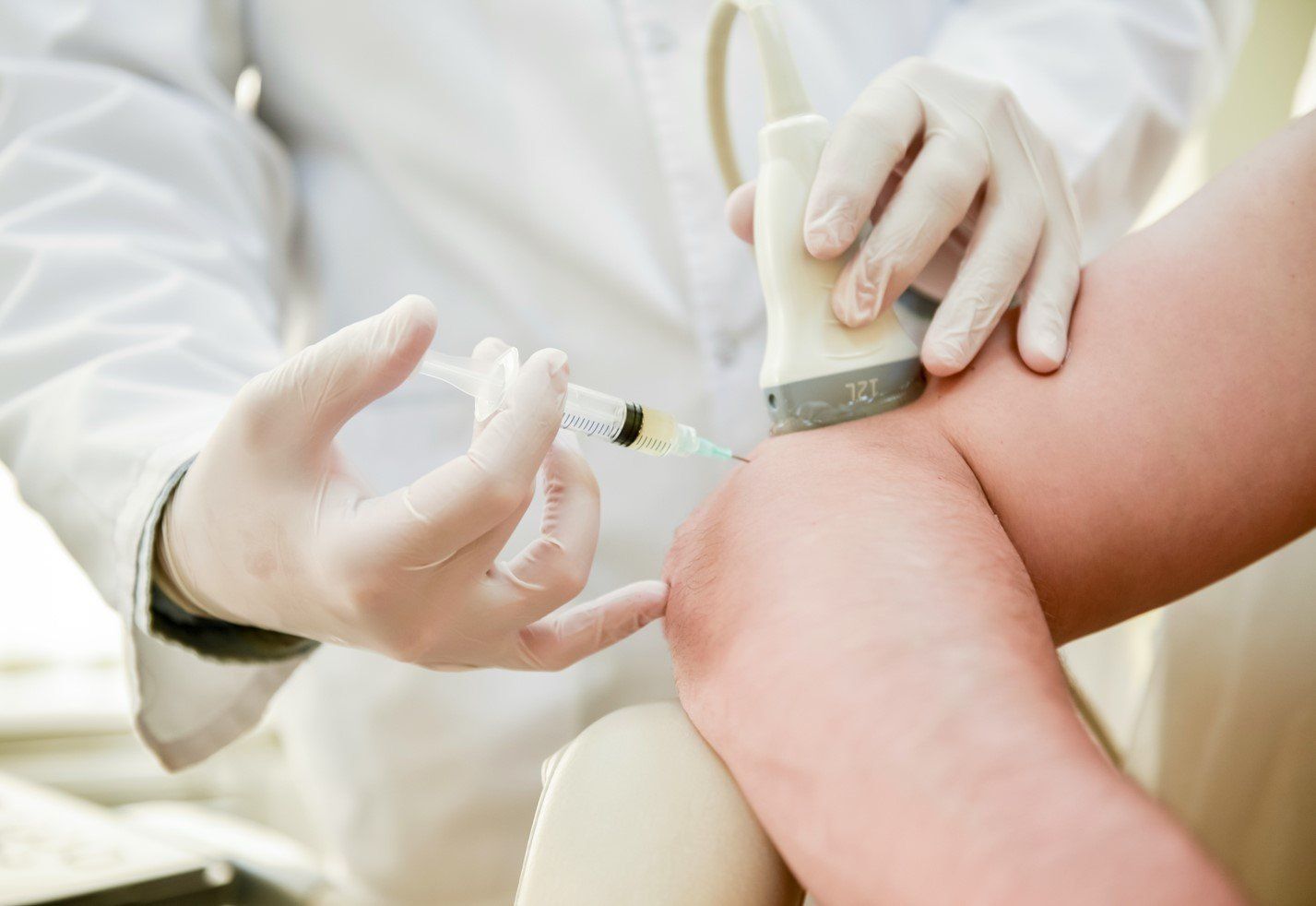
Ultrasound Guided Injections
Specifically Targeting the Source
Most musculoskeletal conditions, once correctly diagnosed, will respond well to relative rest, modification of exacerbating factors and rehabilitation exercise.
However, when progress cannot be made and symptoms are having a negative impact on the ability to engage in rehab, adjunctive treatments can be helpful. Injections for musculoskeletal conditions vary in their mechanism of action.
- For conditions involving chronic inflammation or scar tissue (such as recurrent ankle sprains or chronic bursitis), corticosteroid injections are useful. They do not assist with long term healing.
- For joints with cartilage wear and pain (osteoarthritis), hyaluronic acid injections can provide months of relief
- For certain ligaments and stabilizing tissues that have been injured or stretched, autologous products may be helpful in assisting new collagen formation.
When we are trying to utilize specific treatments for specific problems, it is important to deliver the injection specifically to the correct tissue. Ultrasound guidance not only improves safety of injections by allowing identification of nerves and vessels to be avoided, but it also maximizes the accuracy of the injection to the target tissues.
At progressive sports medicine, we use the latest ultrasound technology to accurately guide injections.
What is the Evidence on Ultrasound-Guided Injections?
The research on whether ultrasound-guided injections are superior to landmark injections for musculoskeletal conditions has shown varying results. While ultrasound guidance has been associated with certain advantages, such as improved accuracy and visualization, the overall superiority may depend on the specific context, the skill of the practitioner, and the targeted anatomical site. It's essential to consult the latest literature for the most up-to-date information.
Here are some key references that discuss this topic:
Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided versus Blind Intra-Articular Injection in Hip Joints of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients:
- Reference: Zhao J, et al. (2018). Ultrasound-guided versus blind injection for MR arthrogram in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a diagnostic accuracy study. Pediatric Rheumatology, 16(1), 12.
- Link: Ultrasound-Guided vs. Blind Injection
- Findings: The study focused on hip injections and suggested that ultrasound guidance improved the accuracy of intra-articular injections, particularly in the context of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Ultrasound-guided versus landmark-guided corticosteroid injection for plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials:
- Reference: Zhang B, et al. (2018). Ultrasound-guided versus landmark-guided corticosteroid injection for plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE, 13(8), e0202703.
- Link: Ultrasound vs. Landmark Injection for Plantar Fasciitis
- Findings: This meta-analysis suggested that ultrasound-guided injections might be more effective than landmark-guided injections for corticosteroid injections in the treatment of plantar fasciitis.
Ultrasound-guided versus landmark-guided local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis:
- Reference: Kuo TT, et al. (2018). Ultrasound-guided versus landmark-guided local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 99(4), 766-775.
- Link: Ultrasound vs. Landmark Injection for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Findings: The systematic review and meta-analysis suggested that ultrasound-guided injections might offer better short-term relief for carpal tunnel syndrome compared to landmark-guided injections.
It's important to note that while some studies show potential advantages of ultrasound-guided injections, the evidence is not universally consistent across all musculoskeletal conditions. Additionally, the skill and experience of the practitioner in performing either type of injection can significantly impact the outcomes.